CNC 铣床是现代制造业的基石,能够以无与伦比的精度对金属、塑料和其他材料进行成型和精炼。但 CNC 铣床到底是什么?它是如何工作的?它与车床等其他 CNC 机床有何不同?更重要的是,使其如此有效运行的关键部件是什么?
从本质上讲,CNC 铣削是一种减材加工工艺,使用旋转切削刀具逐渐从工件上去除材料。这些机器广泛应用于航空航天、汽车、医疗和精密工程等行业。随着技术的进步,CNC 铣床现在具有多轴功能、自动换刀装置和先进的冷却系统,从而以前所未有的方式提高了效率和准确性。
了解 数控铣床 对于任何参与制造的人来说都至关重要。在本指南中,我将分解使这些机器平稳运行的基本要素,从主轴和工作台到控制系统和切削刀具。无论您是 CNC 加工新手还是希望加深专业知识,本文都将为您提供 CNC 铣床组件及其功能的全面概述。
CNC(计算机数控)机器按照预先编程的指令运行,以精确切割、塑形或雕刻金属、木材、塑料和复合材料等材料。该过程从 CAD(计算机辅助设计)文件开始,工程师或设计师在其中创建所需部件的详细 2D 或 3D 模型。然后使用 CAM(计算机辅助制造)软件将此数字蓝图转换为 G 代码,该软件将设计转换为控制 CNC 机器运动的特定命令。将程序加载到机器的控制器后,操作员将原材料固定在机器的工作台上并选择合适的切削刀具。当 CNC 机器开始运行时,它会沿多个轴(基本机器的 X、Y 和 Z 轴,更复杂的机器的附加 A、B 和 C 轴)移动,以极其精确地遵循编程路径。高速电机、滚珠丝杠和先进的传感器确保准确定位和平稳运行。根据 CNC 机器的类型,无论是铣床、车床、刨床、等离子切割机、激光切割机,还是 3D 打印机;该工具要么去除材料(减材制造),要么添加材料(增材制造)来塑造最终产品。在整个过程中,自动监控系统跟踪加工进度,以确保一致性和质量。加工完成后,零件可能需要额外的精加工工艺,如打磨、去毛刺或抛光,然后进行最终质量检查,通常使用坐标测量机 (CMM) 或激光扫描仪来验证准确性。CNC 机器通过提供高精度、可重复性和高效率彻底改变了现代制造业,使其成为航空航天、汽车、医疗和电子制造等行业必不可少的机器。
CNC 铣床由多个部件组成,这些部件共同执行加工操作。每个部件在确保铣削平稳和精确方面都发挥着至关重要的作用。以下是 CNC 机床主要部件的细分:
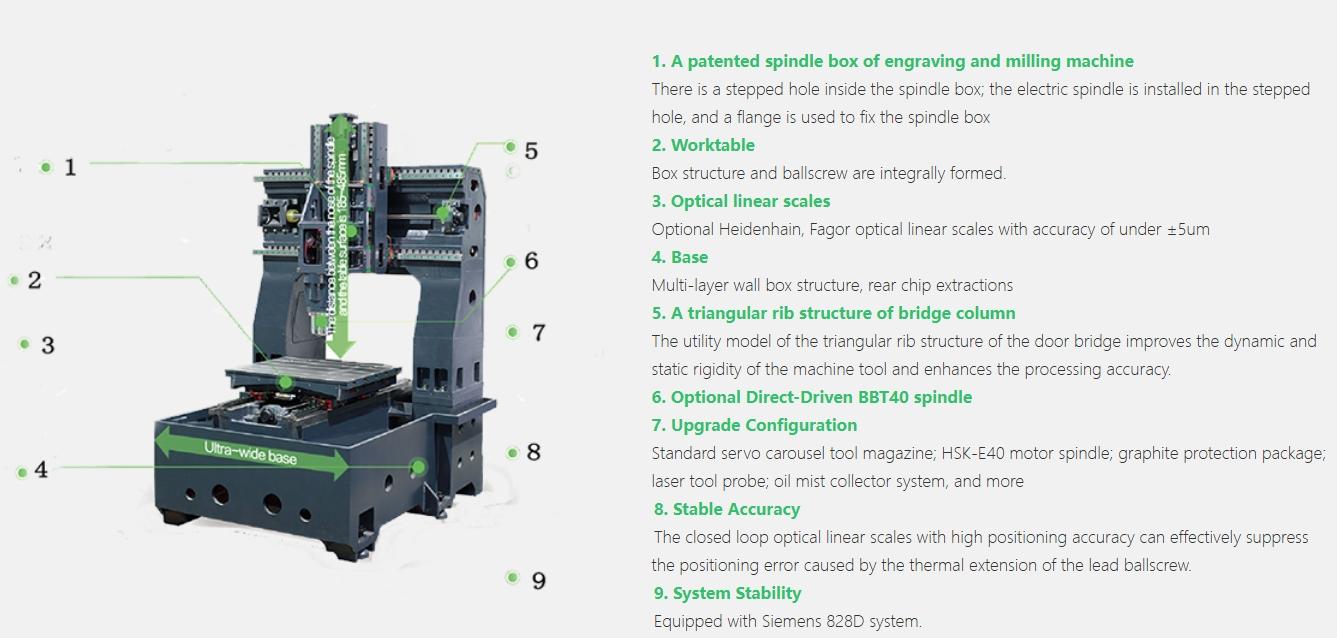
CNC 控制器是机器的大脑。它解释 G 代码并通过向步进电机或伺服电机发送信号将其转换为精确的动作。这消除了手动操作的需要,使机器更高效并减少人为错误。
柱子和底座构成了 数控铣床。它们通常由铸铁制成,具有刚性和稳定性,可减少切削过程中的振动。底座支撑整个机器,而立柱容纳冷却液和油系统等重要部件。
支腿是与立柱连接的可调节垂直部件。它使工作台能够垂直移动,从而使铣刀能够到达工件的不同高度。
鞍座位于膝部上方,可沿 X 和 Y 轴移动,从而正确定位工件以进行加工。
CNC 机床使用机电进给机构来控制铣床的三维运动。该机构由根据 CNC 程序执行运动的电机驱动。
工作台是放置工件的平面。它包括 T 型槽,有助于使用夹具或虎钳固定材料。一些先进的机器提供混合工作台,支持 CNC 铣削和等离子切割。
主轴是固定和驱动铣刀的旋转部件。主轴通常由高碳铬钢制成,可根据材料和操作以各种速度运行。
铣削夹头将切削刀具牢牢固定到位。它由可拧紧或松开以适应不同刀具的夹爪组成。
在立式数控机床中,主轴箱是支撑铣头的可移动臂。主轴箱可以前后移动,从而提高加工的灵活性。
在卧式 CNC 铣床中,悬臂取代了主轴。它支撑着将铣刀固定到位的心轴。
心轴支架固定心轴和切削刀具,确保切削操作过程中的稳定性和减少振动。

附件可提高 CNC 铣床的性能、安全性和效率。一些常见的附件包括:
冷却液系统通过在切削区域喷洒冷却液来防止过热。这可以减少摩擦、防止刀具磨损并改善表面光洁度。冷却液可以是水基(用于减少热量)或油基(用于润滑)。
动力牵引杆可以自动拧紧或松开工具,从而减少手动更换工具所需的时间。
安全罩是一种防护屏障,可防止碎屑、灰尘和冷却液飞溅到机器外部。这可提高操作员的安全性。
旋转套件可实现 4 轴加工,可铣削圆柱形或曲面。这对于雕刻和复杂零件制造至关重要。
自动换刀装置 (ATC) 根据 CNC 程序自动切换工具,非常适合需要多种工具的复杂加工任务。
碎屑托盘可收集金属或材料碎屑,防止堆积并使清理更容易。
机器防护装置保护运动部件以防止事故发生,符合 ISO 13849 安全规定。
CNC 铣床根据操作和材料使用不同的切削刀具。这些刀具通常由高速钢 (HSS) 或硬质合金制成,以提高耐用性。
立铣刀是最常见的铣削刀具。它们有不同的形状和尺寸,适用于特定操作:
● 平头铣刀:用于一般切割。
● 球头立铣刀:用于轮廓和 3D 形状。
● 圆角立铣刀:非常适合减少零件角落的压力。
面铣刀用于使表面平整并提供光滑的表面。
粗铣刀可以快速去除大量材料,使其成为初始切削阶段的理想选择。
槽钻用于在材料上切割槽和凹槽。
飞刀用于精加工操作并产生极其光滑的表面。
螺纹铣刀用于切削材料中的内螺纹或外螺纹。
铰刀可以扩大孔并提高精度。
虽然 CNC 铣床可以进行钻孔,但有时也会使用专用钻头来钻孔。
CNC 铣床的价格根据其尺寸、功能和附加功能而有很大差异。入门级机器的价格可能只有几千美元,而高端工业机型的价格则高达数十万美元。
对于希望投资合适设备的企业和制造商来说,了解影响 CNC 铣床价格的关键因素至关重要。以下是影响 CNC 铣床成本的八个最重要的因素。
机床工作台的尺寸是影响其价格的主要因素之一。数控铣床的工作台尺寸各不相同,从小型台式机型到能够处理大型工件的大型工业机床。
● 更大的工作台可以加工更大的零件,这使得它们对于航空航天和汽车等行业至关重要。
● 桌子越大,意味着需要的建造材料就越多,从而增加了总体成本。
● 大型数控铣床需要更强大的电机和刚性结构,以在广阔的工作范围内保持精度。
例子:
配有 12" x 18" 工作台的小型台式 CNC 铣床的价格可能约为 5,000 美元,而航空航天中使用的大型 60" x 120" CNC 铣床的价格可能超过 150,000 美元。
主轴是 CNC 铣床的核心,负责高速旋转切削刀具。主轴的额定功率不同,通常以马力 (HP) 或千瓦 (kW) 为单位。
● 更高功率的主轴可以加工更硬的材料,如钢、钛和因科镍合金。
● 具有强力主轴的机器具有更强劲的电机,需要更好的冷却系统和耐用的轴承,从而增加了成本。
● 高 RPM(每分钟转数)主轴(例如 30,000 RPM 主轴)价格更昂贵,但可为精细加工提供更好的精度。
例子:
● 适用于软金属和塑料的3 HP 主轴成本较低。
● 用于航空航天应用的15 HP 高速主轴成本要高得多。
CNC 铣床的刚性直接影响精度、耐用性和成本。具有刚性框架的机器在加工过程中振动较小,可确保切割准确且使用寿命更长。
● 材质成分: 由铸铁或钢制成的机器稳定性更好,但价格也更昂贵。
● 重量和加固: 重型框架提供更好的精度,但需要 制造成本更高.
● 振动控制: 刚性框架可减少工具颤动并提高表面光洁度质量。
例子:
轻质铝框架 CNC 铣床价格实惠,但对于重型应用而言稳定性较差。相比之下,钢框架工业 CNC 铣床精度更高,但成本要高得多。
CNC 机床在运行过程中可容纳和自动更换的刀具数量会影响生产率和成本。CNC 铣床配有手动或自动换刀系统 (ATC)。
● 带有手动换刀功能的基本 CNC 铣床价格较便宜,但会降低生产速度。
● 配备 ATC 的机器可以在几秒钟内在多种工具之间切换,从而提高了效率,但也降低了成本。
● 更大的刀库(可容纳 10、20 甚至 100 多个刀具)需要更复杂的控制系统,因此成本更高。
例子:
3 工具 CNC 铣床的成本明显低于 20 工具容量的工业 CNC 铣削中心,后者由于自动化,成本可能高达 50,000 美元。
CNC 铣床根据其可移动的轴数量进行分类:
● 3 轴 CNC 铣床:沿 X、Y 和 Z 轴移动(最实惠)。
● 4 轴 CNC 铣床:增加围绕一个轴的旋转,允许进行更复杂的切割。
● 5 轴 CNC 铣床:增加围绕两个轴的旋转,使其成为复杂航空航天或医疗组件的理想选择,但会显著增加成本。
● 更多轴需要先进的电机和控制器来同步运动。
● 旋转台和多轴控制软件等更高精度的组件会增加总体成本。
● 提高灵活性和自动化程度使得只需一次设置即可加工复杂的零件,从而降低了劳动力成本。
例子:
● 一台三轴 CNC 铣床的成本可能在 10,000 至 50,000 美元之间。
● 配备复杂软件和硬件的 5 轴 CNC 铣床起价可能为 100,000 美元以上。
CNC 控制系统是机器的大脑,负责解释 G 代码并控制运动。不同品牌和型号的控制器功能和价格各不相同。
● 处理速度: 高速处理器缩短了循环时间但增加了机器成本。
● 用户界面: 具有 3D 模拟功能的直观触摸屏控制器价格更高。
● 品牌声誉: Fanuc、Siemens、Haas 和 Heidenhain 控制器是高端控制器,而 Mach3 或 GRBL 等基本控制器则更便宜。
例子:
一个基本的 Mach3 控制器要花费几百美元,而一个先进的西门子 840D CNC 控制器则要花费几千美元。
知名品牌的数控铣床由于其声誉、质量和售后支持而往往价格更高。
例子:
一台普通的中国数控铣床可能要花费 5,000 美元,而一台 Mazak 5 轴数控机床由于其卓越的品质和可靠性可能要花费 250,000 美元。
CNC 铣床可以定制配件以提高效率和精度。这些附加组件会增加总体成本。
● 冷却液系统:通过减少热量来延长工具寿命。
● 旋转套件:启用附加运动轴。
● 外壳和安全功能:提高工作场所的安全性。
例子:
添加自动冷却系统可能会额外花费 2,000 美元,而完整的机器外壳可能会增加 5,000 美元或更多。
数控铣床对于精密制造至关重要,其效率取决于其组件、配件和工具。投资合适的机器需要评估工作台尺寸、主轴功率、框架刚度和自动化功能。虽然入门级 CNC 铣床适合小型企业,但高端工业 CNC 铣床最适合大规模生产。了解这些因素将帮助您选择最适合您需求的 CNC 铣床。